One of the most famous and appreciated jewels, rings, adorn the delicate hands of ladies and sometimes gentlemen and carry an ancient and fascinating history.
The significance and symbolism of the ring are important for most people, as the ring is commonly used as a symbol of devotion, loyalty, eternity, and divinity.
Ring Symbolism in Antiquity
Ring symbolism is rich and vast, especially in Ancient Greece.
Prometheus, freed by Heracles, had accepted to wear an iron ring with a piece of stone on his finger as a reminder of the rock and the chains of the Caucasus, where he had been chained into eternal punishment by Zeus.
The ring in this myth has a double symbolism. First, is Prometheus’ submission to Zeus. Secondly, the ring evokes that, sometimes, greatness and punishment are linked to each other. The stone of that ring, if it is not a seal, is a signature.
Apart from Prometheus’ ring, there is also the story of Polycrates’ ring.
According to this legend, Polycrates was such a fortunate king that, convinced his luck could not last forever, he decided to voluntarily sacrifice a precious object to the goddess of luck, Fortuna.
Climbing a high tower, he threw a ring adorned with a beautiful emerald into the sea. Once in the water, the ring was swallowed by a fish, which in turn was fished by a fisherman, and the ring was returned to Polycrates.
Polycrates’ precious jewel was destined to protect from bad luck, locking it in a magic circle, but the sea refused to accept the ring Polycrates sacrificed.
Moreover, soon after this event, king Darius waged war against Polycrates, who was defeated and died tied to a cross.
In this way, the Polycrates’ ring symbolizes the destiny from which man cannot escape.
Polycrates wanted to sacrifice the jewel as compensation for his incredible fortune, but the gods only accepted only what they were determined to take.
Ring Symbolism in the Roman Era
At the beginning of the Roman Republic, the first rings were forged from iron. Each ring had a seal, the signature of the one who wore it. Seals were used to sign or authenticate important documents.
The right to wear gold rings, jus annuli aurei, was initially granted only to senators and only when they had the duties of Republic ambassadors.
Over time, however, this rule was abolished, and the right to wear gold rings was granted to all Roman citizens.
During the Roman Empire’s glory period, men and women wore massive gold rings decorated with very expensive precious stones.
That was how the rich and powerful could display their privileged status.
So we can see how, throughout history, the ring has served as a symbol of loyalty, eternity, divinity, and social status.
Whether a ring is made of iron, gold, or adorned with precious stones, it is a powerful representation of an unbreakable bond between two people, a reminder of the eternal oath of love and fidelity.
The Significance of Rings and their Symbolism in Ancient Egypt
In Ancient Egypt, rings held exceptional importance, particularly those featuring the scarab motif.
Most of the jewelry made during that period, including rings, displayed the scarab, which was considered a sacred beetle that symbolized life and rebirth.
These scarab rings were carved in various precious and semi-precious stones such as lapis lazuli, amethyst, turquoise, or crystal. They were then engraved with decorative hieroglyphs, protective symbols, or noble titles for high society members.
With its ring symbolism, this elevated the simple gold or silver ring into a valuable jewelry piece and a lucky or protective amulet.
During the New Kingdom period (1559-1085 BC), Egyptian jewelers developed advanced working techniques, allowing them to create more complex objects.
Among the most impressive rings of that period were the royal seal rings, which served as obvious symbols of rank and power and as means of authenticating official documents.
The scarab and other religious motifs were also common in these rings.
However, the ring symbolism and importance for the ancient Egyptians were more comprehensive than that of the rings mentioned above.
Priests and ordinary people wore rings set with religious motifs. Although these rings were equally decorated with semi-precious stones and complex motifs, they were not worn for their value but as talismans or for religious purposes.
Moreover, a more profound symbolism is associated with the fingers on which the rings were worn.
What's the Meaning of the Finger You Wear a Ring On?
The meaning of the finger you wear a ring on is old and dates back to the ancient Romans, for whom the ring was a symbol of wealth, power, wisdom, and a bond with the gods.
Rings could signify different meanings when worn on different fingers.
Ring symbolism when worn on the little finger: It has Mercury as its tutelary God and expresses cleverness, communication, and intuition. The ring worn on the little finger may also symbolize brilliant intelligence.
Ring symbolism when worn on the finger’s ring: It has Apollo as its tutelary God and expresses creativity. The ring worn on the ring finger may symbolize spiritual energy in all its forms.
Ring symbolism when worn on the middle finger: It has Saturn as its tutelary God and reflects the concept of good and evil, as well as the idea of justice. The ring worn on the middle finger symbolizes introspection, secrets, and mystery.
Ring symbolism when worn on the index finger: It has Jupiter as its tutelary God and expresses power and authority. The ring worn on the index finger denotes self-confidence and ambition.
Ring symbolism when worn on the thumb: It has no tutelary god but expresses self-affirmation, personal, and universal will. A ring on this finger can signify the desire for commitment and ambition.

Ring Symbolism: Understanding the Significance of Engagement Rings
Engagement rings have been the subject of many interpretations and debates due to their significance and relevance to our daily lives.
They are part of a rich cultural history that dates back to ancient times and remains essential in modern times.
Ring symbolism has been significant in many cultures throughout history, where the ring served as a symbol of authority, respect, and love.
For example, the Fisherman’s Ring was used as a pontifical seal and represented the exclusive bond of the Pope.
On the other hand, the engagement ring symbolizes a bond that connects two people and is often viewed as a pledge of love and commitment.
The use of rings as a symbol of respect and authority is mentioned in several chapters of the Bible.
In Genesis 41:41, Pharaoh took his signet ring and put it on Joseph’s hand as a symbol of his authority.
Rings were often worn as decorations in Ancient Greece, Rome, and even among less civilized European populations.
In Ancient Ireland, a man who wanted to marry a woman would give her a bracelet woven from human hair. Accepting the bracelet, the woman approved the marriage and forever bound herself to the man.
This ritual was part of a solemn engagement that preceded the wedding.
In the Middle Ages, the engagement ceremony was considered the most significant event in the wedding.
The engagement ring was typically made of bronze, wood, or even clay. The man offering the ring was also required to demonstrate his wealth and ability to care for his wife.
However, in the 9th century, Pope Nicholas I demanded the engagement ring be made exclusively out of gold. Later, in 1215, Pope Innocent III allowed rings made of any metal, including iron and silver.
The ring symbolism, especially the engagement ring symbolism, had many interpretations over the years.
The mere iron ring, given by the fiancé to the bride’s family at the engagement, represented his financial ability and commitment. The bride then had the duty to submit to the man and listen to him until the end of her life.
Later, the groom would give the bride two rings, one made of gold for festivities and the other made of iron, intended to be worn at home.
The ring symbolizes a faithful, freely accepted connection in the Christian tradition.
It is linked to time and the cosmos, and its significance goes beyond its physical appearance.
Pythagoras once said, “Do not put the image of God on your ring,” implying that God should not be associated with time.
The first Christians wore rings following the example of pagans, but only knights had the right to wear a gold ring. Clement of Alexandria advised his contemporaries to engrave the image of a dove, a fish, or an anchor on their ring stone.
Esoterically, the ring was endowed with magical powers.
It represented a reduced model of the girdle, keeper of a treasure, or a secret. Putting a ring on one’s finger or passing it on to someone else meant keeping it for oneself or accepting the gift given by another as an exclusive or reciprocal treasure.
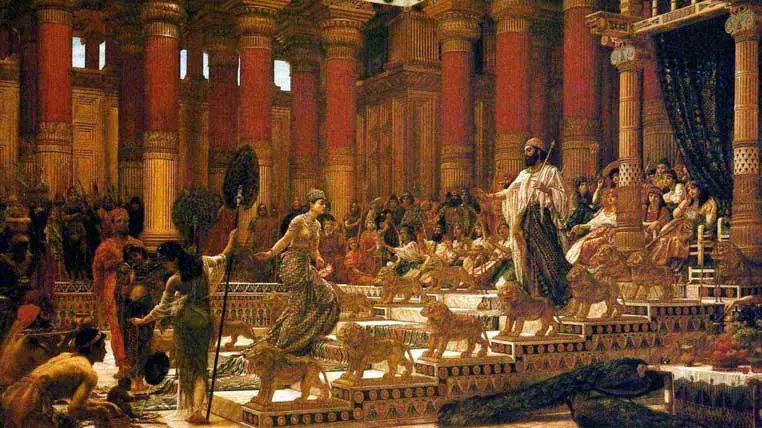

Ring Symbolism: The Legendary Ring of King Solomon
Throughout history, rings have served as symbols of recognition, power, and bonds. They have played a significant role in stories, novels, dramas, songs, and legends.
One of the most famous legends is the story of King Solomon and his wisdom ring.
It is said that the ring bestowed upon him his profound knowledge. According to Arab folklore, King Solomon used the seal on his ring to mark the demons he had gathered for his magic, thus making them his slaves.
However, when he lost his ring in the Jordan River, he sought help from a fisherman to recover his precious possession. Without his ring, King Solomon believed his kingdom would collapse and be overrun by enemies.
Some esoteric authors have suggested that King Solomon’s Ring was stolen by a jealous genie who used it until the day God forced him to throw it into the sea, allowing Solomon to recover it.
King Solomon’s ring symbolism is also interesting.
The ring represented Solomon’s knowledge and power over other beings, like a seal of fire, a gift from the heavens, a sign of his spiritual and material dominion.
In England, rings were exchanged to seal verbal contracts of engagement.
In Italy, rings were popularly used, and the diamond was the preferred precious stone for engagement rings.
Even today, diamonds remain the favorite gemstone for engagement rings, and many believe diamonds are intrinsically linked to these kinds of jewelry.
According to an old superstition, the brilliance of diamonds originates from the fires of love. As such, the engagement ring with a diamond is considered the only authentic engagement ring, signifying love and happiness in the couple for the rest of their lives.
At Ancient Theory we only use trusted sources to document our articles. Such relevant sources include authentic documents, newspaper and magazine articles, established authors, or reputable websites.
- Rod-and-ring symbol - wikipedia.org. [Source]
- Rings: Ancient to Neoclassical - langantiques.com.
- Budge E. A. Wallis - Amulets and Talismans. Collier Books, New York, 1970.
- Eichler Lillian - The Customs of Mankind. Doubleday, New York, 1937.
- Ring - wikipedia.org. [Source]
- Nelson Felicitas - Talismans & Amulets of the World. Sterling Publishers, New York, 2000.
- Elizabeth J. Roop - History and Meaning of Symbolic Rings. Ball State University, Muncie, Indiana, 2011.
- Douglas S. LeGrand - Early History of Jewelry: Ancient Times to the 17th Century.






